문자열 2 - Trie
Trie
Tire(트라이) 란?
Trie는 문자열을 효율적으로 저장하고 검색하기 위한 '트리' 형태의 자료구조이다.
- 메모리를 많이 사용하는 대신, 탐색속도가 매우 빠르다.
- 주로 자동완성, 사전, IP 라우팅 등에 사용된다.
Trie의 구조
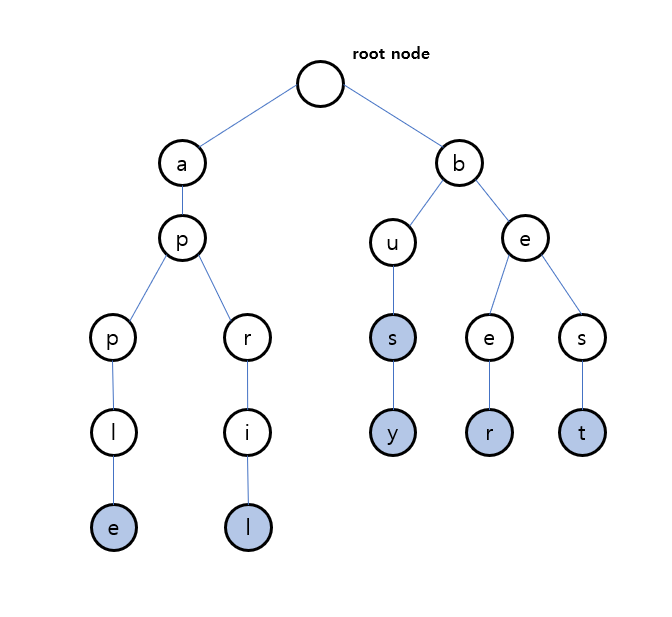
- 루트 노드는 빈 문자열을 나타내야 하므로 항상 비어있어야한다.
- 각 노드는 문자(
Character) 1개를 가진다. - 각 노드는 '현재 노드를 마지막으로 하는 단어가 있는지' 를 나타내는
isEndOfWord라는boolean타입 필드를 가진다.- 위 그림에서 파란색 노드가
isEndOfWord = true - 즉, 위 그림에서 담고 있는 문자열은
apple,april,bus,busy,beer,best이다.
- 위 그림에서 파란색 노드가
복잡도
시간 복잡도
- 삽입: - 은 문자열 길이
- 검색:
- 삭제:
공간 복잡도
- - N은 문자열 개수, M은 평균 길이
- 문자의 종류: ex) 알파벳 - 26개
장단점
장점:
- 문자열 검색이 매우 빠르다.
- 정렬된 순서로 문자열을 순회할 수 있다.
단점:
- 메모리 사용량이 많다.
구현
노드 구조
class TrieNode {
Map<Character, TrieNode> children;
boolean isEndOfWord;
public TrieNode() {
children = new HashMap<>();
isEndOfWord = false;
}
}
전체 자료 구조
class Trie {
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// 탐색 메서드
// 삽입 메서드
// 삭제 메서드
}
탐색
class Trie {
...
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode current = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
if (!current.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return false;
}
current = current.children.get(ch);
}
return current.isEndOfWord;
}
...
}
삽입
class Trie {
...
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode current = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
current.children.putIfAbsent(ch, new TrieNode());
current = current.children.get(ch);
}
current.isEndOfWord = true;
}
...
}
삭제
물리적 삭제 포함
class Trie {
...
public boolean delete(String word) {
return delete(root, word, 0); // root 부터 삭제 재귀적으로 진행
}
private boolean delete(TrieNode current, String word, int index) {
if (index == word.length()) { // 지우려는 문자열과 같은 길이 이며
if (!current.isEndOfWord) {
return false; // 삭제 실패
}
// 지우려는 문자열이 존재할 경우 isEndOfWord == true
current.isEndOfWord = false; // false로 만들어 지운다. (논리적 삭제)
return current.children.isEmpty(); // 이 노드는 자식이 없으니 삭제해도 돼! (물리적 삭제)
}
char ch = word.charAt(index); // 현재 문자
TrieNode node = current.children.get(ch); // 현재 문자에 대응하는 자식 노드
if (node == null) { // 대응하는 자식 노드가 없다면 삭제할 문자열이 없는 것임
return false;
}
// 다음 문자로 재귀적으로 호출
boolean shouldDeleteCurrentNode = delete(node, word, index + 1);
// 만약 물리적으로 삭제해도 된다면
if (shouldDeleteCurrentNode) {
current.children.remove(ch); // 현재 노드에서 해당 자식노드와 연결 제거
return current.children.isEmpty() && !current.isEndOfWord; // 현재 노드도 삭제 가능한지 반환 (자식이 없고, 다른 단어의 끝이 아닐 때)
}
// 자식 노드를 삭제하지 않으므로 현재 노드도 유지
return false;
}
...
}
- 결국 단순하게 생각하면
isEndOfWord를false로 바꾸면 되지만, 메모리 최적화를 위해서 이를 물리적으로도 삭제 해야할지 판단해서 삭제하는 코드이다. - 조금 복잡해서 주석을 코드마다 달아놨다.
- 코딩 테스트에서는 어짜피 최대 메모리 제한만 있고 실시간 메모리 최적화 여부는 판단하지 않으니, 그냥
isEndOfWord만false로 바꾸어도 될 것 같다.
논리적 삭제만
class Trie {
...
public boolean delete(String word) {
TrieNode current = root; // 삭제할 단어의 마지막 노드까지 이동
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
if (!current.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return false; // 단어가 존재하지 않음
}
current = current.children.get(ch);
}
// 단어의 끝이 아니면 삭제 실패
if (!current.isEndOfWord) {
return false;
}
// isEndOfWord만 false로 변경 (논리적 삭제)
current.isEndOfWord = false;
return true;
}
...
}